As the positive electrode material of energy storage batteries, lithium iron phosphate(LFP) has great advantages in safety performance and cycle life, which are also one of the most important technical indicators of power batteries. LFP has good safety performance, long cycle life, high energy density, and is environmentally friendly. Compared with lead-acid batteries, which have low initial costs and high maintenance costs, lithium iron phosphate batteries have high initial costs, but low maintenance costs. Generally, household energy storage systems can maintain a good operating level with little manual maintenance.
But low maintenance cost is relative, no matter what type of battery, it is very sensitive. Especially in the process of using the battery, it is inevitable that there will be a loss. Due to the difference in the external environment and the way of use, the degree of this loss is also different. Through professional maintenance, the battery loss can be minimized, thereby prolonging the service life of the battery.
When using an LFP battery energy storage system, what are the specific points that need to be paid attention to? Below we list some points that need attention for the maintenance and maintenance of the energy storage system to help you extend the service life of the energy storage system as much as possible.
Maintain proper working temperature
The operating temperature range of lithium iron phosphate battery is extensive (-20°C-75°C), but this does not mean that the working state of the battery at different temperatures within the interval is the same. Generally speaking, the ambient temperature of the energy storage system is kept at 15°C-35°C. At this temperature level, the battery can fully release the capacity while avoiding damage to the battery capacity.
The low-temperature performance of lithium iron phosphate batteries is poor. If lithium iron phosphate batteries work and charge and discharge in a low-temperature environment for a long time, metal lithium will be precipitated on the surface of the battery anode. This process is irreversible and will cause permanent damage to the battery capacity.
The discharge capacity of the lithium iron phosphate battery at a temperature of 0 to -20°C is equivalent to 88.05%, 65.52%, and 38.88% out of the discharge capacity at a temperature of 25°C, respectively. That is to say, as the temperature decreases, the average discharge voltage and discharge capacity of lithium-ion batteries decrease, and the lower the temperature, the more obvious the decrease.
Although the high-temperature performance of the lithium iron phosphate battery is very good, too high a temperature can easily cause corrosion inside the battery, which will also affect the working performance of the battery. Therefore, to keep the battery at a suitable working temperature, the installation location of the energy storage system is very important.
Avoid long shelving
When a lithium battery is left unused, self-discharge, passivation of positive and negative electrode materials, and decomposition of electrolytes will occur due to the nature of the battery itself. However, the unstable SEI performance of the negative electrode will lead to the rapid decline of the negative electrode active material, and the precipitation of lithium metal is easy to occur, and this process is also irreversible.
Avoid overcharging and discharging
For lithium iron phosphate batteries, over-discharging and over-charging will damage the battery's capacity. The way to use the lithium battery correctly is to charge it when the power is not enough, avoid recharging when the power is exhausted, and avoid overcharging. Under normal circumstances, we recommend that you charge the device when the power is used below 20%.
Maintain battery consistency
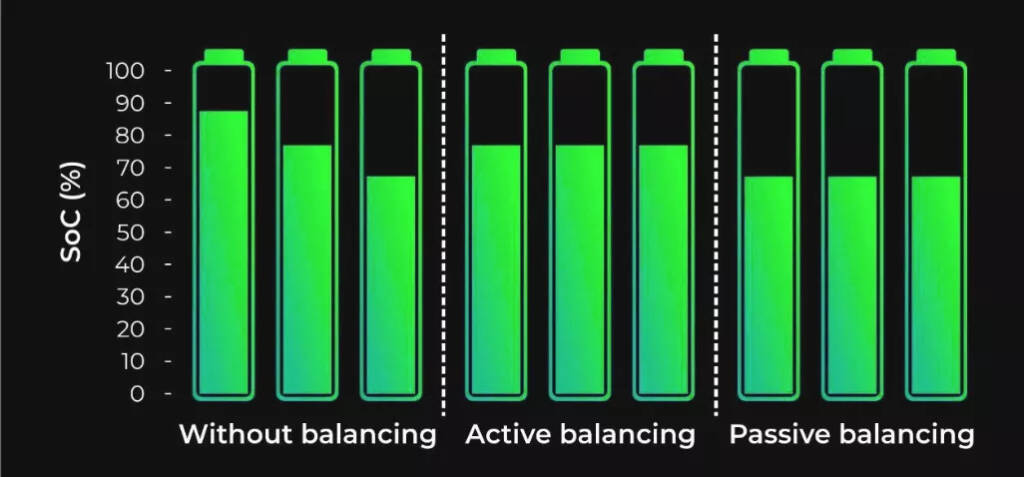
Usually, the battery packs of our energy storage products are realized by connecting single cells in series and parallel. Due to its characteristics, the lithium battery pack has high requirements for the consistency of the monomers. As long as one of the batteries in a group is different from the other batteries, the overall effect will be greatly reduced. Similar to the principle of wooden barrels, inconsistent single batteries are used in series, and the life of the battery pack is always shorter than that of the shortest single battery.
Therefore, we do not recommend that you mix new and old batteries or different types of batteries. However, with the use of the battery, there will inevitably be inconsistencies between the individual batteries. At this time, it is necessary to balance the states of different batteries through equalization.
Avoid external impact
Some families place heavy objects on the energy storage battery for convenience. However, if the weight of the item is too high, mechanical deformations due to material penetration, crushing, and bending may occur in the long run. Mechanical deformation is also often one of the causes of thermal runaways, which can lead to fires. In addition, excessive external temperature, excessive charging and discharging, and internal circuit short circuits also usually easy to cause thermal runaway. So we have to eliminate the triggers at the outset.
In general, the service life of lithium batteries is mainly affected by two aspects, one is the external use conditions, and the other is the factors of the internal batteries.
From the perspective of external use conditions, the factors that affect the service life of lithium batteries mainly include charge and discharge methods, charge and discharge cut-off voltage, charge and discharge rate, use temperature, and storage conditions.
From the perspective of internal battery factors, the use of lithium batteries on ESS is often in the form of battery packs. Battery packs generally connect hundreds of battery cells in series and parallel. The consistency of the cells is another important factor affecting service life. The main performance is the inconsistency of parameters such as voltage, capacity, and internal resistance.
Therefore, after understanding the factors affecting the service life of lithium batteries, solving these problems can greatly improve the cycle life of lithium batteries, and the service life of lithium iron phosphate batteries with better maintenance can reach more than 10 years.
- 3C batteries (1)
- 48C Advanced Energy Project Credits (1)
- ActiveBalancing (1)
- Advanced Storage Solutions (1)
- advanced technologies (1)
- African market (1)
- AI Algorithms (1)
- AI in Energy Storage (1)
- air conditioning (1)
- All-in-One Energy Storage (1)
- American electricity market (1)
- ancillary services market (1)
- application scenarios (2)
- Arnstadt (1)
- automotive industry (1)
- backup generators (1)
- Backup power (1)
- batteries (2)
- Battery Discharge (1)
- Battery Energy Storage (1)
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (1)
- Battery Energy Storage Systems (BESS) (1)
- battery factory (1)
- battery industry event (1)
- battery management system (3)
- battery management systems (1)
- battery market (1)
- battery materials (1)
- battery pack (1)
- Battery Storage Safety (1)
- Battery technologies (1)
- battery technology advancements (1)
- battery type (1)
- BatteryLongevity (1)
- BatteryManagementSystem (1)
- BatterySafety (1)
- BatteryTechnology (1)
- BESS (1)
- Birmingham Exhibition (1)
- BMSArchitecture (1)
- Brazil energy storage (1)
- Burkina Faso (1)
- Capacity (1)
- capacity rule (1)
- carbon management (1)
- carbon neutrality goals (1)
- CATL (1)
- CE marking (1)
- certification (1)
- certifications (1)
- Charge Current (1)
- Charge/Discharge Rate (1)
- Chemical Storage (1)
- China electricity market (1)
- China International Battery Fair (1)
- CIBF 2023 (1)
- Clean energy (6)
- clean energy incentives (1)
- Clean Energy Revolution (1)
- clean energy solutions (1)
- Climate Goals (1)
- Climate Legislation (1)
- Commercial (1)
- Commercial Energy Storage (2)
- CompleteCurrentControl (1)
- Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) (1)
- consumer batteries (1)
- Containerized Energy Storage (1)
- Continuous Discharge Duration (1)
- conversion efficiency (1)
- Cooperation (1)
- cost composition (1)
- cost parity (1)
- cost reduction (1)
- Cost-effective storage (1)
- critical power (2)
- CSA certification (1)
- Customized Energy Storage (1)
- DC bus voltage (1)
- Decarbonization (1)
- Decarbonized future (1)
- Demand Forecasting (1)
- Department of Energy (1)
- DesignConsiderations (1)
- development strategies (1)
- Direct Pay (1)
- Discharge Current (1)
- discharge curve (1)
- Distributed Energy (1)
- Dongguan Lithium Valley (2)
- dual carbon goal (1)
- Dubai World Trade Center (1)
- efficient energy storage (1)
- Electric Vehicle Charging (1)
- Electric Vehicles (2)
- Electricity Costs (1)
- Electricity Infrastructure Operations Center (1)
- electricity market (1)
- electricity price mechanism (1)
- electricity prices (1)
- electricity supply (1)
- electrochemical energy storage (1)
- Electrochemical Storage (1)
- Energy Certification (1)
- Energy Community Adder (2)
- energy companies (1)
- energy consumption (1)
- energy consumption management (1)
- energy crisis (1)
- Energy Demand (1)
- Energy Demands (1)
- energy density (2)
- energy distribution (1)
- Energy Efficiency (1)
- energy industry (1)
- Energy Industry Solutions (1)
- energy investment (1)
- Energy Landscape (1)
- Energy Management System (3)
- energy management systems (1)
- energy professionals (1)
- energy sector (1)
- energy solutions (2)
- Energy storage (16)
- Energy Storage Batteries (3)
- Energy storage battery business (1)
- Energy Storage Battery Industry (1)
- Energy Storage Battery Technology (1)
- energy storage business model (1)
- Energy Storage Cabinets (1)
- energy storage capacity (1)
- Energy Storage Certification (1)
- Energy Storage Challenges (1)
- energy storage components (1)
- energy storage converters (1)
- energy storage equipment (1)
- Energy Storage Incident (1)
- energy storage industry (4)
- energy storage market (1)
- Energy Storage Products (1)
- energy storage profitability (1)
- energy storage projects (1)
- Energy storage research (1)
- Energy Storage Solution (2)
- Energy Storage Solutions (4)
- Energy Storage System (3)
- energy storage system solutions (1)
- Energy Storage Systems (5)
- Energy Storage Technologies (2)
- Energy Supplies (1)
- Energy Supply Challenges (1)
- Energy Transition (1)
- energy trends (1)
- EnergyEfficiency (1)
- EnergyStorage (1)
- Environmental Innovation (1)
- environmental sustainability (1)
- ESS chain (1)
- EU countries (1)
- European battery factory (1)
- European electricity market (1)
- European Market (1)
- European Solar Market (1)
- Exhibitors (1)
- Extended Tax Credits (1)
- field study (1)
- financing options (1)
- fire protection systems (1)
- Flexibility (2)
- Flow batteries (2)
- Flywheel Energy Storage (1)
- Fossil Fuel Emissions (1)
- fossil fuels (1)
- generation side (1)
- Germany (2)
- Gigawatts (1)
- Global Carbon Emissions (1)
- global energy storage (1)
- global market share (1)
- global power batteries (1)
- government officials (1)
- Government Support (1)
- granular silicon (1)
- Green Energy Initiatives (1)
- Green Living (1)
- Green Technology (2)
- Greenhouse Gas Emission Verification (1)
- grid (1)
- Grid reliability (2)
- grid resilience (1)
- grid side (1)
- Grid Stability (3)
- Grid Storage Launchpad (1)
- grid voltage (1)
- grid-connected (1)
- Guide (1)
- high-voltage battery (1)
- higher discharge rate (1)
- Home Energy Storage (3)
- Home Energy Storage Benefits (1)
- household energy storage (2)
- hydropower (1)
- I&C energy storage (1)
- IEC 62619 (2)
- IEEE 1547 (1)
- inductive loads (1)
- Industrial (1)
- industrial and commercial energy storage (1)
- industrial and commercial track (1)
- Industrial Energy Storage (6)
- Industry Trends (1)
- IndustryStandards (1)
- Inflation Reduction Act (1)
- Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) (1)
- installed energy storage (1)
- integrated energy storage cabinet (1)
- integration (1)
- intelligent solutions (1)
- Intermittency (1)
- International Energy Agency (1)
- International Energy Agency (IEA) (1)
- International Energy Storage Exhibition (1)
- Intersolar (1)
- Intersolar Europe 2023 (1)
- Intersolar Middle East (1)
- Intertek (1)
- inverter (2)
- inverter power (1)
- Investment (1)
- Investment Tax Credits (1)
- ISO 14001 (1)
- ISO 9001 (1)
- ITC (1)
- Johannesburg (1)
- large size silicon (1)
- large-scale energy storage (1)
- Leveraging Solar Power (1)
- life cycles (1)
- LiFePO4 batteries (1)
- lithium batteries (1)
- lithium iron phosphate batteries (2)
- Lithium Prices (1)
- Lithium Valley (14)
- Lithium Valley Products (1)
- Lithium Valley Technology (1)
- Lithium-ion alternatives (1)
- Lithium-Ion Batteries (3)
- lithium-ion battery cells (1)
- lithium-ion voltage (1)
- load capacity (1)
- Long Beach California (1)
- Long Duration Energy Storage (1)
- Long-duration storage (2)
- Low-carbon Future (1)
- low-voltage battery (1)
- LS Energy Solutions (1)
- M&A project (1)
- manufacturing equipment (1)
- Market Opportunities (1)
- market-oriented (1)
- Mechanical Storage (1)
- MEE (1)
- merger agreement (1)
- Microgrids and Distributed Energy (1)
- Middle East Energy Summit (1)
- Mobile Energy Storage (1)
- Multiple-MPPT (1)
- Na+ battery (1)
- Net Zero Emissions (2)
- Netherlands (1)
- new energy battery technology (1)
- Next-generation batteries (1)
- North America (1)
- NREL (1)
- off-grid (1)
- oil and gas (1)
- operating efficiency (1)
- optical storage (1)
- Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (1)
- PassiveBalancing (1)
- Peak Times (1)
- peak-valley price difference (1)
- Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Power (1)
- photovoltaic components (1)
- photovoltaic installations (1)
- plug-and-play (1)
- policy certainty (1)
- polysilicon (1)
- power batteries (1)
- power battery company (1)
- power battery developments (1)
- power conversion system (1)
- power density (1)
- Power Generation (2)
- power match (1)
- power supply (1)
- power system (1)
- power systems (1)
- power transmission (1)
- Power/Energy (1)
- Predictive Analytics (1)
- Product Carbon Footprint Certificate (1)
- product line (1)
- product upgrades (1)
- production capacity (2)
- production process (1)
- profit model (1)
- Pumped Hydro Storage (1)
- quality management system (1)
- R&D team (1)
- raw materials (1)
- regional energy transformation (1)
- Reliability testing (1)
- Reliable Power Supply (1)
- renewable energy (18)
- renewable energy capacity (1)
- Renewable Energy Industry (1)
- Renewable energy integration (2)
- renewable energy investment (1)
- renewable energy policies (1)
- renewable energy production (1)
- Renewable Energy Revolution (1)
- Renewable Energy Solutions (1)
- renewable energy sources (1)
- Renewable Energy Storage (1)
- RenewableEnergy (1)
- renewables sector (1)
- Residential & Commercial Energy Storage (1)
- residential energy storage (2)
- rural energy storage (1)
- safer energy storage (1)
- Sandton Convention Centre (1)
- Scalability (1)
- service life (1)
- shadow scan function (1)
- signing ceremony (1)
- silicon materials (1)
- silicon wafers (1)
- single-cluster battery management (1)
- Single-MPPT (1)
- smarter energy storage (1)
- SNEC Exhibition (1)
- Sodium-ion batteries (1)
- Sodium-ion Battery (1)
- Solar & Storage Live 2023 (1)
- Solar Capacity (1)
- solar cells (1)
- Solar Energy (2)
- Solar Energy Industry (2)
- solar energy products (1)
- solar energy storage (1)
- Solar Energy Technologies (1)
- Solar Generation (1)
- Solar Installations (1)
- solar integration (1)
- solar modules (1)
- solar panel energy storage (1)
- solar power (2)
- Solar PV (1)
- Solar Show Africa 2023 (1)
- Solar Sustainability (1)
- solar trends (1)
- Solar-Plus-Storage Integration (1)
- Solid-State Batteries (1)
- South African Minister of Energy (1)
- Stacked High-Voltage Battery (1)
- standardization (1)
- StateEstimation (1)
- Storage Installations (1)
- Storage Ratio (1)
- Storage Systems (1)
- Strategy Director (1)
- SUMEC (1)
- Supplier Conference (1)
- supply chain cost (1)
- Supply Chain Traceability (1)
- surge power (1)
- Surplus Energy (1)
- Sustainability (1)
- Sustainable Development (1)
- Sustainable Energy (2)
- Sustainable Future (1)
- Sustainable Power Grid (1)
- sustainable power solutions (1)
- Sustainable Practices (1)
- Sustainable Technology (1)
- SustainableEnergy (1)
- system structure (1)
- TD (1)
- technical components (1)
- Technological Innovation (2)
- technology exchange (1)
- Temporary Power Solutions (1)
- ternary lithium batteries (1)
- Thermal Storage (1)
- Thuringia (1)
- Transferability (1)
- transparent reporting (1)
- TUV certification (1)
- Types of Energy Storage Systems (1)
- UK (1)
- UK Legislation (1)
- UL 1973 (2)
- UL 9540A (1)
- US Federal Government (1)
- US manufacturers (1)
- US public investments (1)
- user side (1)
- Utilities (1)
- voltage match (1)
- wholesale market (1)
- Wind Capacity (1)
- Wind Energy (1)
- Wind Generation (1)
- Wind Installations (1)
- wind power (1)
- winter energy demand (1)
- Zero Emissions (1)
- Zonsen Power (1)
- ZZonsen Power (1)

